Hey there, friend! Let’s dive into something wild and unpredictable—weather tornadoes. You might think of tornadoes as just a chaotic swirl of wind and debris, but there’s so much more to it. They’re like nature’s version of a high-speed blender, and understanding them can save lives. So, buckle up, because we’re about to explore the science, the danger, and the awe-inspiring power of these twisters. And trust me, you’re gonna want to keep reading.
Weather tornadoes aren’t just random acts of nature. They follow patterns, and scientists have spent decades studying them to figure out how they form, why they strike certain areas, and how we can prepare for them. Whether you’re living in Tornado Alley or just curious about the weather phenomena that shape our planet, this article is your ultimate guide to everything tornado-related.
Now, before we get too deep into the nitty-gritty, let’s set the stage. Tornadoes can be terrifying, but they’re also fascinating. Imagine a funnel cloud touching down, tearing through trees, flipping cars, and leaving behind a trail of destruction. But it’s not all doom and gloom. Understanding tornadoes gives us the power to predict them better and protect ourselves and our communities. Ready to learn more? Let’s go!
Read also:Wsdot Your Ultimate Guide To Washington State Transportation
Table of Contents
- What Are Tornadoes?
- How Do Tornadoes Form?
- Tornado Classification
- Tornado Alleys
- Tornado Season
- Safety Tips During a Tornado
- Common Tornado Myths
- A Brief History of Tornadoes
- Famous Tornadoes Around the World
- Future Predictions for Tornado Activity
What Are Tornadoes?
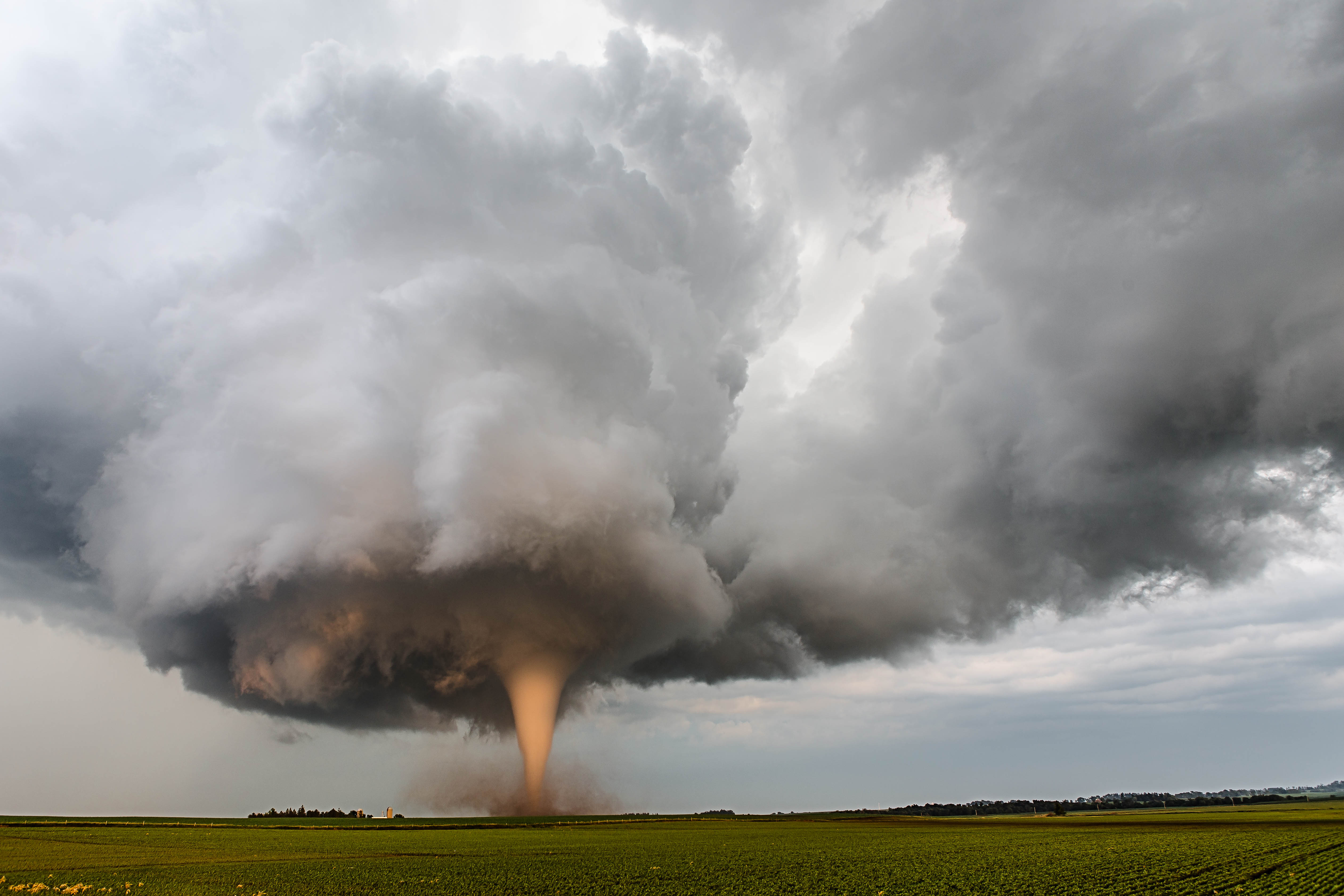
So, what exactly are tornadoes? Simply put, they’re violently rotating columns of air that extend from a thunderstorm to the ground. They’re like nature’s ultimate power tool, carving paths of destruction wherever they go. And yeah, they’re pretty scary, but they’re also a natural part of our weather system.
Tornadoes are often referred to as twisters or cyclones, depending on where you’re from. In the U.S., they’re mostly called tornadoes, but in other parts of the world, they might be known by different names. Regardless of what you call them, they’re all about one thing—powerful winds that can reach speeds of over 300 mph!
Why Study Tornadoes?
Understanding tornadoes is crucial because they pose a significant threat to life and property. They can strike without much warning, especially in areas prone to severe weather. By studying their behavior, scientists can improve forecasting models, giving people more time to seek shelter and stay safe.
Plus, learning about tornadoes is just plain cool. Ever wondered how a funnel cloud forms? Or how a tornado can lift a car into the air like it’s nothing? Stick around, and we’ll break it all down for you.
How Do Tornadoes Form?
Alright, let’s talk about the science behind tornado formation. It’s not as simple as just wind blowing around. Tornadoes require specific conditions to form, and it all starts with thunderstorms. Specifically, supercell thunderstorms are the ones to watch out for.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the process:
Read also:The Good American Family Celebrating Tradition Values And Modernity
- Warm Moist Air: Tornadoes need warm, moist air near the surface to fuel their formation.
- Cool Dry Air: Above the warm air, you need cooler, drier air. This creates instability in the atmosphere.
- Wind Shear: Changes in wind speed and direction with height help create rotation in the atmosphere.
- Updrafts and Downdrafts: Strong updrafts in the storm lift the rotating air, eventually forming a funnel cloud.
Once all these factors come together, you’ve got yourself a tornado. It’s like a recipe for chaos, but it’s also a beautiful example of nature’s complexity.
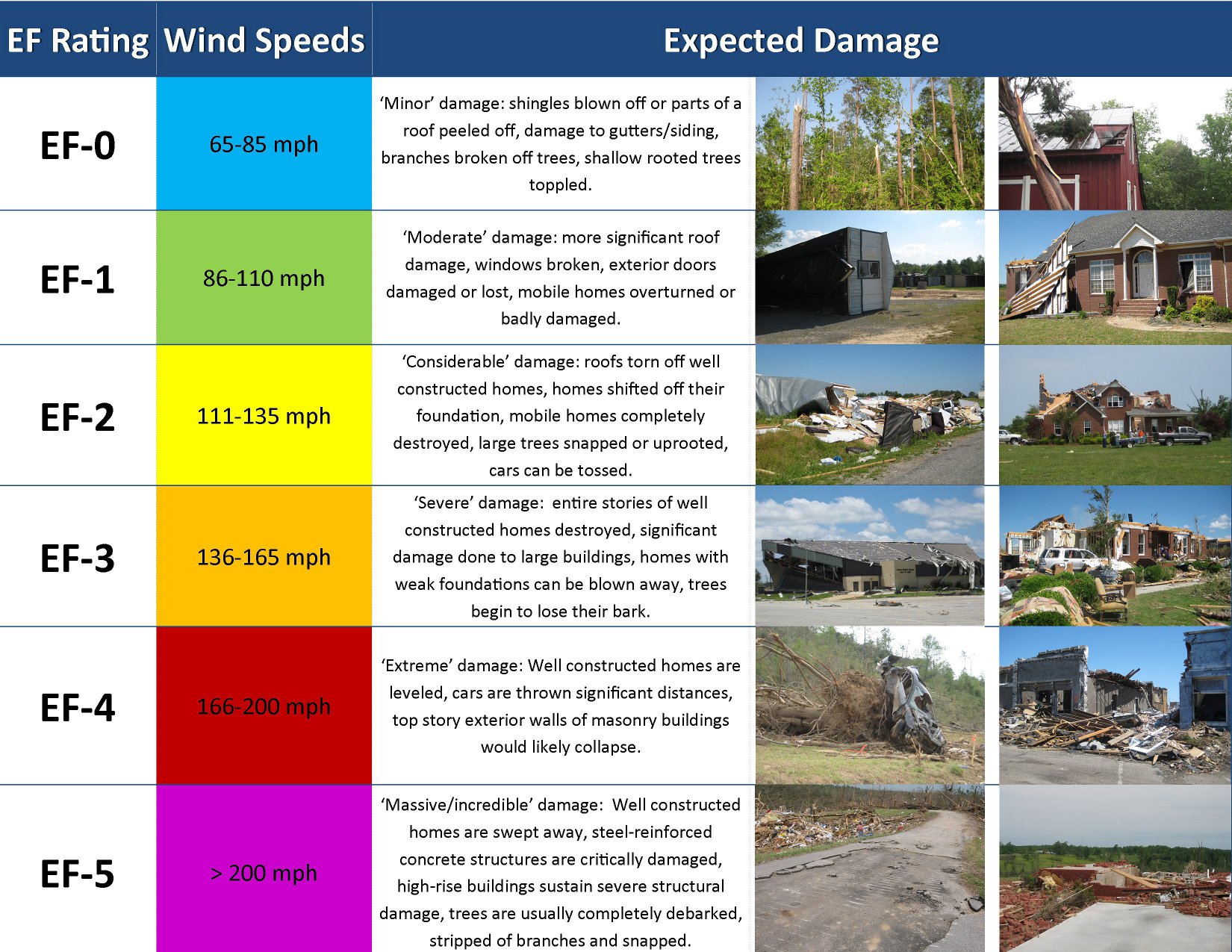
Tornado Classification
Not all tornadoes are created equal. They come in different sizes, shapes, and intensities. To help categorize them, meteorologists use the Enhanced Fujita (EF) Scale. This scale ranges from EF0 to EF5, with EF5 being the strongest and most destructive.
Here’s a quick rundown of the EF Scale:
- EF0: Winds up to 85 mph. Minor damage to buildings, broken tree branches.
- EF1: Winds 86-110 mph. Roofs peeled off, mobile homes overturned.
- EF2: Winds 111-135 mph. Significant damage to houses, large trees snapped.
- EF3: Winds 136-165 mph. Entire stories of homes destroyed, trains overturned.
- EF4: Winds 166-200 mph. Well-constructed homes leveled, cars thrown.
- EF5: Winds over 200 mph. Total destruction of buildings, debris flying everywhere.
Knowing the classification of a tornado can help you gauge its potential impact and take appropriate action.
Tornado Alleys
If you’ve ever heard of Tornado Alley, you know it’s a hotspot for tornado activity. But what exactly is it? Tornado Alley refers to a region in the central United States where tornadoes are most frequent. States like Texas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Nebraska are often mentioned in this context.
Why does Tornado Alley exist? It’s all about geography and climate. The flat plains of the central U.S. provide the perfect conditions for tornado formation. Warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico meets cool, dry air from the Rockies, creating the perfect storm—literally.
Other Tornado Prone Areas
While Tornado Alley gets all the attention, other parts of the world also experience frequent tornadoes. For example, Bangladesh and parts of Europe have their own versions of Tornado Alley. Each region has its own unique set of conditions that contribute to tornado formation.
Tornado Season
Tornado season is a term used to describe the time of year when tornadoes are most likely to occur. In the U.S., this typically happens during the spring and early summer months. However, tornadoes can happen at any time of the year if the conditions are right.
Here’s a breakdown of tornado season across different regions:
- Spring: Peak tornado season in the southern U.S.
- Summer: Tornado activity shifts northward.
- Fall: A secondary peak in tornado activity, especially in the Southeast.
- Winter: Rare, but tornadoes can still occur in certain areas.
Understanding tornado season can help you prepare for potential threats and stay safe.
Safety Tips During a Tornado
Now, let’s talk about the most important part—staying safe during a tornado. Whether you’re at home, at work, or out and about, knowing what to do can make all the difference.
Here are some essential safety tips:
- Seek Shelter: If you’re in a building, go to the lowest level and find an interior room without windows.
- Stay Low: If you’re outside and can’t find shelter, lie flat in a ditch or low-lying area.
- Protect Yourself: Cover your head with your hands or a blanket to protect against flying debris.
- Stay Informed: Keep a weather radio or smartphone handy to stay updated on warnings.
Remember, seconds count during a tornado, so having a plan in place can save your life.
Common Tornado Myths
There are plenty of myths surrounding tornadoes, and it’s time to set the record straight. Here are a few common ones:
- Myth #1: Tornadoes can’t cross rivers. Fact: Tornadoes can and do cross rivers. The 1927 Tri-State Tornado crossed the Mississippi River.
- Myth #2: Opening windows will equalize pressure and prevent damage. Fact: This is not true and can actually make things worse.
- Myth #3: Tornadoes only happen in the U.S. Fact: Tornadoes occur all over the world, though the U.S. sees the most.
By busting these myths, we can better prepare for tornadoes and avoid dangerous misconceptions.
A Brief History of Tornadoes
Tornadoes have been a part of human history for centuries, though our understanding of them has evolved over time. Early records of tornadoes date back to the 17th century, with accounts of destructive twisters in Europe and North America.
One of the most famous tornado outbreaks occurred in 1925, known as the Tri-State Tornado. It traveled across Missouri, Illinois, and Indiana, causing widespread destruction and claiming hundreds of lives. This event helped shape modern tornado research and forecasting efforts.
Advancements in Tornado Research
Over the years, scientists have made significant advancements in tornado research. From radar technology to storm-chasing vehicles, we now have tools that allow us to study tornadoes up close and improve our ability to predict them.
Famous Tornadoes Around the World
While the U.S. is famous for its tornadoes, other parts of the world have also experienced devastating twisters. Here are a few notable ones:
- Dhaka Tornado (1989): One of the deadliest tornadoes ever recorded, it struck Bangladesh and killed over 1,300 people.
- Elie Tornado (2007): Canada’s first EF5 tornado, it caused significant damage but no fatalities.
- Moore Tornado (2013): An EF5 tornado that devastated Moore, Oklahoma, causing billions in damage.
These events highlight the global impact of tornadoes and the importance of international cooperation in disaster preparedness.
Future Predictions for Tornado Activity
As our climate continues to change, scientists are studying how it might affect tornado activity. While it’s still unclear whether climate change will lead to more frequent or stronger tornadoes, some models suggest we might see shifts in tornado patterns.
One thing is certain—advancements in technology will continue to improve our ability to forecast and respond to tornadoes. From AI-powered weather models to drones that can fly into the heart of a storm, the future of tornado research looks promising.
In conclusion, weather tornadoes are both a force of nature and a reminder of our vulnerability. By understanding them, we can better prepare for their impact and protect ourselves and our communities. So, the next time you hear a tornado warning, remember what you’ve learned here and stay safe!
Final Thoughts
Weather tornadoes are a fascinating and powerful phenomenon that deserve our respect and attention. From their formation to their destructive potential, there’s so much to learn. By staying informed and prepared, we can minimize the risks and maximize our chances of surviving a tornado encounter.
So, what do you think? Did we cover everything you wanted to know about tornadoes? Leave a comment below and let us know. And if you found this article helpful, don’t forget to share it with your friends and family. Together, we can spread awareness and make a difference!